A 3D scanner is used to scan objects in three dimensions and import the scanned model to software (user-preferred) where post-processing and alteration is carried out, before producing a model to be sent to a 3D printer.
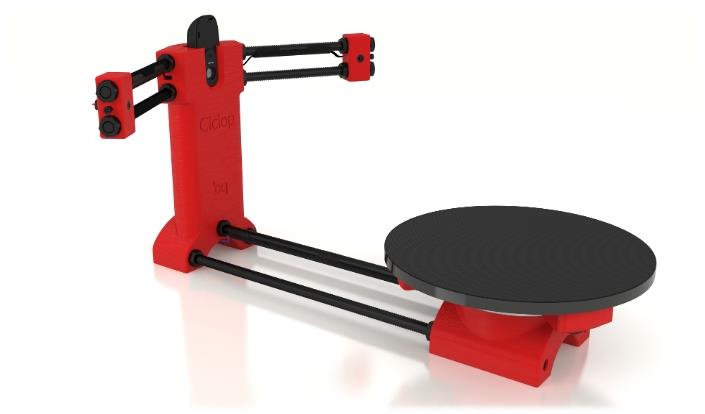
As a part of Graduate research and development projects at PowerEarth, we are well on the way to develop a fully functional 3D scanner. This 3D scanner will allow us to scan objects of the size 400x400x450mm. It will utilise both photogrammetry and laser scanning technology.
This technology is the same as used by most high end commercially available 3D scanners. However, these are often acquired at a budget that outweighs the benefits of the scanner.
We have developed all the basic components of the scanner using:
– Two-line lasers
– A stepper motor
– A webcam
– An Arduino UNO controller
– A scan expansion board
– Associated driving board
– 3D printed components (open source from Thingiverse) using PowerEarth’s in house high volume 3D.
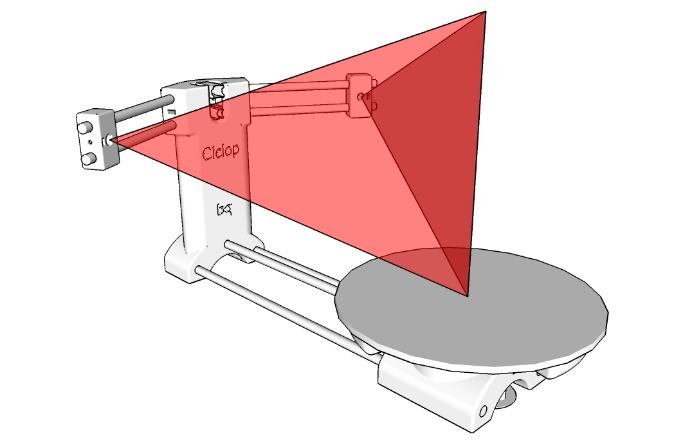
The basic working principle behind the developed 3D scanner is, that after placing the object on a stepper motor controlled disk, the embedded camera scans the object illuminated from two-line lasers. These lasers are positioned at pre-defined angles for each rotational position on the disk.
The main software used in the above process is called HORUS. HORUS is an open-source software that has the capability to ensure communication between the computer and the 3D scanner. HORUS is essential for calibration as well as image processing.
Open-Source 3D scanner

Photogrammetry and laser scanning technology
Parts required/printed for 3D scanner

To find out more about our exciting development of a fully functional 3D scanner, contact us today for more information.

